Social Media Addiction Statistics
Psychologists estimate that tens of millions of Americans are addicted to social media apps such as Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok. While adults and teens both use the platforms, social media addiction statistics indicate that the younger generation is more easily addicted and more susceptible to negative effects such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts leading to an increase in social media addiction lawsuits.
Since the early 2000s, social media has revolutionized the way we connect with one another. Social media has evolved since the days of Myspace, the very first platform. Dozens of other platforms have since emerged, from Facebook and Instagram to YouTube and TikTok, capturing the attention of larger and larger audiences.
In 2005, just five percent of Americans used social media. By 2024, a staggering 69.7 percent of Americans had active social media accounts.
It’s estimated that more than 4.95 billion people worldwide actively use social media every day. By 2027, nearly six billion people are expected to use social media daily.
However, social media appears to carry some risks. Among them is the risk of addiction.
But just how addictive is social media? How often are people using social media? Who is at the greatest risk of becoming addicted?
Statistics clearly show that social media has become a huge part of our lives. This phenomenon is particularly true for children, teens, and young adults, who spend hours daily using social media.
Here are some of the most staggering stats on social media use and addiction:
- Globally, the average person spends two hours and 27 minutes on social media every day.
- The average American spends two hours and 15 minutes on social media per day.
- It’s estimated that 210 million people worldwide are addicted to social media.
- More than half of all drivers admit to checking social media behind the wheel.
- Overuse of social media in children and teens can literally rewire their brains.
- Roughly 42 percent of teens admit that social media keeps them from connecting with friends in person.
- In a recent survey, 70 percent of teens said they feel left out or excluded because of social media.
- Suicide rates among teens have increased in the age of social media.
- Social media is more addictive than alcohol and cigarettes.
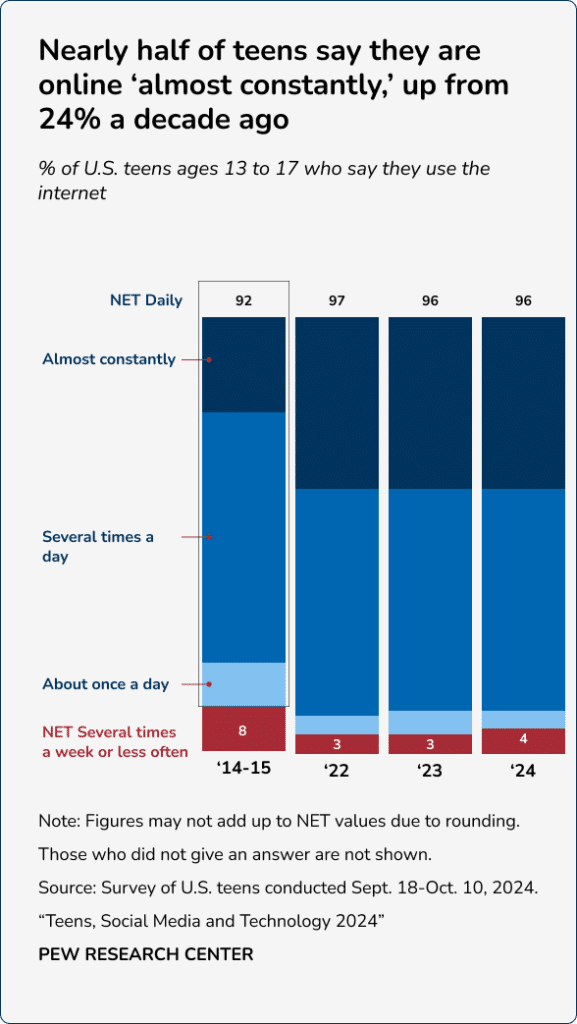
Social media is changing how we live our lives. This is particularly true for children, teens, and young adults, who increasingly spend more time online and less time engaging with friends, family, and peers in real life. In a 2023 Pew Research survey, 46 percent of teens surveyed said their internet use was almost constant.
Research shows that this can have serious and potentially life-changing consequences.
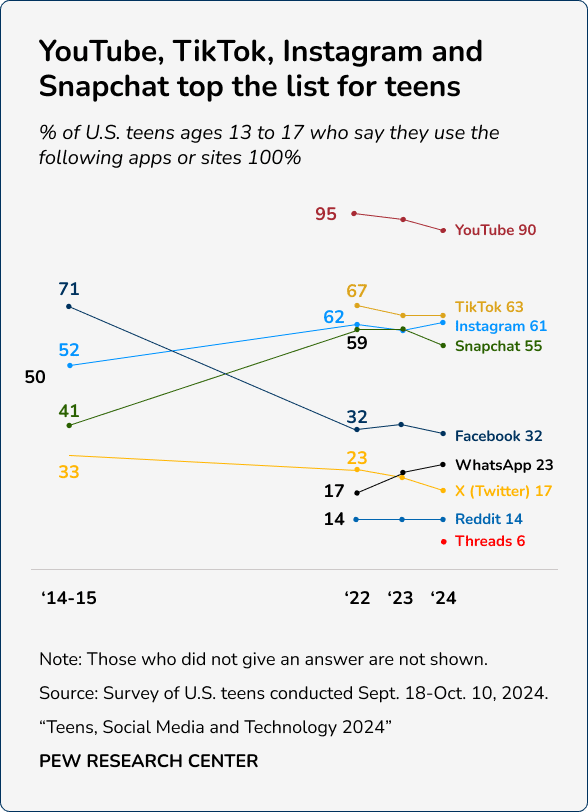
1. YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok are the most popular social media apps among teens.
There are dozens of social media apps vying for the attention of teenagers and adults alike. For many years, Facebook reigned champion, drawing the time and attention of billions of users every day. In fact, seven out of 10 Americans still admit to checking Facebook daily.
However, as social media evolved and teens became more engaged, the most popular—and dangerous—apps changed.
In 2015, 71 percent of teens used Facebook. By 2024, only 32 percent of teens used Facebook.
A 2024 Pew Research Center survey found that YouTube remains the preferred social media site for teens, with roughly nine out of ten of those ages 13 to 17 surveyed using the video-sharing app.
Meanwhile, 63 percent of teens use TikTok, 61 percent use Instagram, and 55 percent use Snapchat.
Other popular apps include WhatsApp at 23 percent, Twitter—rebranded as X in 2023—at 17 percent, Reddit at 14 percent, and Threads at 6 percent.
2. Instagram is the most dangerous social media platform for teens’ mental health.
Nearly two-thirds of American teenagers use Meta’s Instagram. Unfortunately, a recent survey by the U.K.’s Royal Society for Public Health and the Young Health Movement found that Instagram was the most detrimental to mental health among the most popular apps.
Specifically, teenagers between the ages of 14 and 17 noted increased feelings of anxiety, depression, loneliness, and the fear of missing out, or FOMO, when scrolling Instagram. Teens also acknowledged that Instagram interfered with their ability to sleep, contributed to body dysmorphic disorder, and increased instances of bullying.
3. Depression and anxiety in children and teenagers began to rise with the rollout of smartphones.
Research confirms that the more the average young person uses social media, the more likely it becomes that they experience serious mental health issues such as:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Body dysmorphia
- Attention problems
- Loneliness
Experts note that these mental health issues began to increase in children in 2011 and 2012, which was when most people switched to smartphones. In fact, today, roughly 95 percent of teenagers own a smartphone.
This puts social media at their fingertips, giving them access to apps such as Facebook, TikTok, Snapchat, and Instagram without restriction or limitation.
Teenagers who use social media for three or more hours every day are at an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems. Teens who spend between five and seven hours a day using social media are twice as likely to exhibit signs of mental health problems.
This statistic is alarming, considering recent data. According to 2023 survey data from Gallup, young adults between the ages of 13 and 17 spend an average of 4.8 hours on social media daily.
4. Teens, particularly teenage girls, are more likely than adults to be addicted to social media and experience mental health problems.
All teens use social media, but girls spend more time online. Girls are also more likely to become depressed and anxious, develop body image problems and disordered eating behaviors, or become suicidal because of social media.
Research indicates that girls are more likely than boys to become emotionally invested in social media content. According to a 2023 advisory from then-United States Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy, at least one-third of girls aged 11 to 15 said they felt “addicted” to certain social media platforms. Girls are more likely than boys to compare themselves to others and feel bad about themselves if their posts don’t get a lot of likes or aren’t well-received by their peers.
The Surgeon General also reported that nearly half of adolescents aged 13 to 17, regardless of gender, said social media makes them feel worse about their body image.
Researchers have noted that teens are more susceptible to addiction and negative consequences because their brains have not fully developed. They also lack significant real-world experience dealing with other people in social settings.
Teens are growing up in an increasingly digital world, where their lives are spent engaging with others online rather than in person. Adults, on the other hand, have developed social skills through in-person interaction with others.
5. Teen Suicide Rate Increase Correlates to Social Media Usage Increase
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, suicide rates for teenage girls doubled between 2007 and 2015. In 2015, 524 female teens committed suicide, an all-time high. Among males aged 15 to 19, there were 1,537 suicides in 2015.
Despite this, teenage girls still have significantly higher rates of persistent sadness, poor mental health, suicidal ideation, and suicide attempts than their male counterparts in the present. The CDC found that female students were twice as likely as male students to have experienced suicide risk indicators.
In late 2024, the CDC published an updated analysis of mental health and suicide risk among high schoolers based on data from the organization’s 2023 Youth Risk Behavior Survey. The analysis revealed that nearly 40 percent of students experienced persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness, and more than 20 percent of high schoolers had seriously considered attempting suicide within the past year. Close to 10 percent of students had attempted suicide in the last year.
A 2018 study by several U.S. universities found that greater time spent on social media led to an increase in suicidal ideation in depressed teens, which is a major risk factor for suicide attempts.
Today, suicide is the second-leading cause of death in young adults between the ages of 15 and 24. The correlation between the rise of social media and the uptick in suicide rates among teens cannot be ignored.
Social Media Addiction FAQs
How Many Americans Are Addicted to Social Media?
Conservative estimates suggest that roughly 10 percent of Americans are addicted to social media. That translates to 33.19 million Americans based on 2021 population data.
What Qualifies As Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction refers to an uncontrollable, unhealthy dependence on apps such as Instagram, X, Facebook, TikTok, and Snapchat.
People who become addicted to social media experience an intense urge and compulsion to share content and scroll the apps, which takes up an increasing amount of their time and energy.
Even though social media is allegedly “social,” many who suffer from addiction develop antisocial tendencies and mental health problems that interfere with healthy social skills.
How Does Social Media Addiction Affect the Brain?
Social media platforms are designed to create a cycle of chemical releases in users’ brains that make them want to spend more time on the platform. Feedback on social media, such as “likes” and reposts, activates the brain’s reward center by releasing dopamine, a chemical linked to pleasurable activities like social interaction. These platforms are designed to addict users to the feeling of short, repetitive bursts of dopamine.
Which Social Media Is the Most Addictive?
Generally speaking, the more time the average person spends on a social media platform, the more addictive it is. In the United States, the top three most addictive social media platforms are the following:
- TikTok: 53.8 minutes per day
- YouTube: 48.7 minutes per day
- X/Twitter: 34.1 minutes per day
Can Social Media Addiction Be Avoided?
Social media users can certainly limit and restrict their social media use, thereby decreasing the odds of addiction. However, users should not shoulder all of the responsibility for social media addiction. Research suggests that social media use literally rewires the brain and that social media companies such as Meta have used this to keep users hooked and coming back for more.
This deliberate addiction technique is one of the reasons for the increase in social media addiction lawsuits in recent years. Social media users who have experienced serious health problems or lost family members to suicide have begun to fight back and hold social media companies accountable for the harm inflicted by their algorithms.
If you or a loved one has experienced mental health issues because of social media addiction, contact the experienced team at The Lanier Law Firm. Since 1990, we’ve fiercely advocated for injury victims and their families nationwide. We offer a free, no-obligation case evaluation, allowing you to learn about your legal rights and discover how our law firm can help you take a stand.
By submitting this form, you agree to our terms & conditions. Please read the full disclaimer



