Asbestos Lung Cancer
Asbestos is a known carcinogen; exposure to it can cause lung cancer and pleural mesothelioma. The human body cannot break down asbestos fibers when inhaled. Instead, the fibers embed in the lung tissue. Lung cancer forms in the cells, while pleural mesothelioma forms in the lining of the lungs, known as pleura.
Home » National Mesothelioma Law Firm » Mesothelioma Cancer » Asbestos Lung Cancer
What Is the Difference between Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma?
How Does Asbestos Cause Lung Cancer?
What Are the Symptoms of Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer?
How Is Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
How Is a Case of Lung Cancer Determined to Be Asbestos-Related?
What Are the Treatment Options for Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer?
What Is the Difference between Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma?
Lung cancer forms in the cells of the lung itself, while malignant mesothelioma forms in the lining around certain organs. Pleural mesothelioma develops in the lining of the lungs, known as the pleura.
Some epidemiology studies have estimated that asbestos-related lung cancer causes twice as many deaths per year as mesothelioma, but it’s often difficult to determine the cause of particular lung cancer cases since other factors besides asbestos exposure increase risk for this disease.
Asbestos exposure can also lead to other asbestos-related diseases, such as asbestosis. This is a lung disease in which the presence of asbestos fibers leads to scarring throughout the lung, which eventually interferes with its function and makes breathing difficult. Although asbestosis is not a type of cancer, it’s an indication that a patient had significant asbestos exposure and is at risk for asbestos-related cancers.
How Does Asbestos Cause Lung Cancer?
Asbestos fibers are very tiny. When they’re present in the air, they can’t be seen or even smelled. When a person inhales them, the asbestos fibers can become embedded in the lung tissue.
It’s very difficult to break down asbestos; this is why it was so useful in certain industrial applications. When the fibers enter the lung tissue, the body mounts an immune response to try and remove them. However, the fibers are so stable that they cannot be broken down. The body mounts a stronger and stronger immune response, which is sustained over many years. This damages the surrounding tissues, causing changes in the DNA of lung cells that lead those cells to become cancerous.
People with a history of occupational asbestos exposure are at risk for developing asbestos-related diseases or cancer. Their family members may also be at risk since asbestos fibers can be carried home on a worker’s clothing, hair or skin.
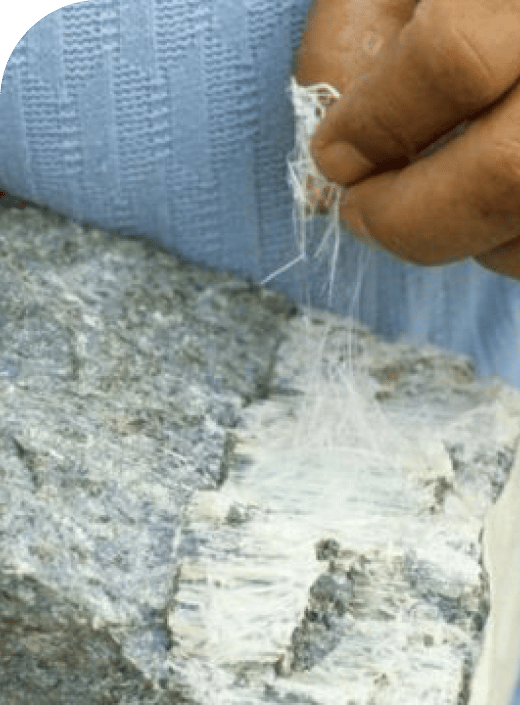

There are two different types of asbestos. Serpentine (also known as chrysotile) asbestos tends to break apart more easily into smaller particles and fibers, and the fibers are curly. Amphibole asbestos (a group that includes the minerals amosite, crocidolite, tremolite, anthophyllite and actinolite) tends to remain in longer fibers, and the fibers are straight.
Both types are associated with lung cancer. This is because the lung tissue is directly exposed to asbestos fibers in the air, so it’s easy for any shape of asbestos fiber to embed itself into the lung tissue. However, the straighter and longer amphibole asbestos fibers are more likely to work their way through the lung tissue into the pleura, so they’re more strongly associated with pleural mesothelioma.
There is no doubt that asbestos exposure is a risk factor for developing lung cancer. Still, cigarette smoking remains the biggest risk factor. Asbestos exposure in non-smokers creates an increased risk for lung cancer, with the risk being about 10 times higher than without asbestos exposure. People who were exposed to asbestos and who also smoke have about 50 times the risk of lung cancer as non-smokers with no asbestos exposure.
What Are the Symptoms of Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer?
- Persistent cough, which may be dry or may sometimes bring up blood
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Excessive fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms are similar to those of many other respiratory diseases, including pneumonia, asthma and COPD (emphysema). Other types of cancer, such as mesothelioma or cancer that has spread from another part of the body may cause the same symptoms.
How Is Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
Imaging studies
- The first step in the diagnostic process is often a chest X-ray.
- Often, a computerized tomography scan (CT scan) of the chest will be used next, although it’s sometimes the first step. A CT scan also uses X-rays but gives doctors a more detailed 3D image.
- Other types of imaging studies may also be used. An MRI uses large magnets to take detailed images, while a PET scan uses a tracer to check for spread of cancer cells throughout the body.
Types of Lung Cancer
- In many lung cancer cases, the sample is obtained through a bronchoscopy. A tube is inserted down the throat and into the lungs to visualize the area and obtain the biopsy sample.
- In some cases, if the tumor is located relatively close to the skin, a transthoracic needle biopsy may be used. A needle is inserted through the chest wall into the lung tissue in order to get the tissue sample.
- Fluid biopsy. In some cases, if a patient has a pleural effusion (a buildup of fluid around the lung), a sample of this fluid may contain enough cancer cells for a pathologist to analyze. There are also cases where sputum samples are collected and analyzed for cancer cells, although this type of analysis can miss many lung cancer cases.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
The cells of SCLC look small and round under the microscope. This type almost always occurs in smokers and is generally harder to treat.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
This includes several subtypes of cancer (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma). The cells of this type are larger, and it’s easier to treat.
Staging of Lung Cancer
The process of staging refers to determining how advanced a cancer is. As part of the process of a mesothelioma diagnosis, doctors will also stage the cancer. For different types of cancer, the stage is described in different ways.
For NSCLC, a system of four stages is generally used, with higher numbers indicating more advanced disease.
- Limited, meaning that the cancer is only in one lung and possibly the lymph nodes in the mediastinum (the center of the chest)
- Extensive, meaning that the cancer has spread beyond this
How Is a Case of Lung Cancer Determined to Be Asbestos-Related?
- The presence of asbestosis
- Pleural plaques (areas of thickening of the pleura) or other changes in the pleura
- Confirmation of the presence of asbestos fibers in the patient’s lung tissue or fluids
- History of asbestos exposure at least 10 years prior (which accounts for the latency period between asbestos exposure and the development of cancer)
Chrysotile asbestos does not tend to accumulate in lung tissue because the fibers can break apart, so significant levels of asbestos may not be found when a tissue sample is examined, even if a patient has had high levels of exposure to chrysotile asbestos. However, patients who have been exposed to amphibole asbestos will often have asbestos fibers found in their lung tissue because the longer fibers tend to embed into tissue and remain for a long time.

What Are the Treatment Options for Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is far more common than mesothelioma. Mesothelioma patients often need to travel to a specific cancer center in order to access an expert on their disease, while lung cancer patients may find oncology experts who are familiar with their disease more readily. Still, many patients are treated at a cancer center in order to more easily access all of the health care that they need.
- Surgery to remove the tumor may be an option for patients in an early stage. This may include removing part of a lung (known as a wedge resection or lobectomy) or even a whole lung (pneumonectomy).
- Chemotherapy can be used in patients who are not eligible for surgery. It can also be used either before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove, or after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to help kill cancer cells that may not have been removed during the procedure.
- Radiation therapy may be used to target a tumor that can’t be removed surgically, before surgery to shrink a tumor, or after surgery to target any cells that may have been left behind.
- Immunotherapy This is a newer treatment option that stimulates the body’s own immune system to destroy cancer cells. The FDA has approved three immunotherapy drugs (Keytruda, Tecentriq and Opdivo) for use in certain patients with NSCLC. Immunotherapy can be used either instead of or in addition to chemotherapy.
Some patients receive palliative care, which is aimed at improving quality of life rather than lengthening life. Patients in more advanced stages may only be eligible for palliative care. Even in earlier stages, some patients choose palliative care because they prefer to be more comfortable in their remaining time rather than enduring the side effects of aggressive treatments.

Clinical Trials
Because lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in the United States, many research studies are being conducted to find better ways of treating this disease. A research study designed to test a new treatment is called a clinical trial.
Some patients choose to enroll in a clinical trial to get access to a cutting-edge new treatment with the potential to extend life or improve quality of life. However, there are no guarantees that the experimental treatment will be better than existing options. If you’re considering being part of a trial, you can search the National Cancer Institute’s database of current clinical trials to find those for which you may be eligible. You should also discuss this issue with your oncologist, who can help you weigh the pros and cons of participating.
By submitting this form, you agree to our terms & conditions. Please read the full disclaimer



