Home » National Mesothelioma Law Firm » Mesothelioma Cancer
Mesothelioma Cancer
Mesothelioma is a rare and serious cancer that affects the mesothelium, or lining, of various organs. You are at risk of developing this cancer if you have been exposed to asbestos. There is a 20-40 year latency between exposure and cancer development. Every year, there are approximately 3,000 new cases of mesothelioma in the United States.
Mesothelioma is a unique disease that affects the lining of either the lung or the lining of the abdominal cavity. Mesothelial cells are a very special kind of cell. The way we’re made, if we normally inhale and exhale, we generally aren’t supposed to feel pain; if we did not have the mesothelial lining, we would. What would happen is our lungs would rub against our rib cage, but because of this lining we’ve got, it’s like an oily Saran wrap; it allows the lung to increase and expand, and decrease, and it allows this movement without it rubbing the rib cage.
Now, that lining, those cells, are the ones that become cancerous in mesothelioma, and it makes it a very difficult disease to treat. I told you that the mesothelial cells, that this lining is see-through like Saran wrap; that’s because it doesn’t really have a blood supply to it. Blood supply makes tissue: red, blue, and other things; this is one where, as a result of no blood supply, it’s really difficult to treat. You can’t really take chemicals like you can for chemotherapy, in a normal way, to treat this. So mesothelioma is a very difficult disease to find any relief from, and it’s a disease that’s not really affecting the lung itself directly, but is doing so indirectly by affecting the lining of the lung or the lining of the abdominal cavity.
approximate number of new mesothelioma cases per year in the U.S.
people in the U.S. are at risk of developing mesothelioma at some point in their lives
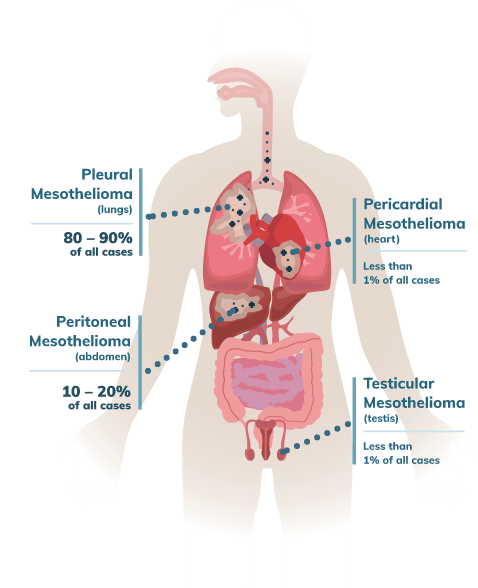
of all cases are pleural mesothelioma which occurs in the lining of the lungs
latency period between asbestos exposure and potential development of mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive type of cancer that occurs in the mesothelium, which is a type of membrane that lines certain organs of the body. The primary risk factor for developing mesothelioma cancer is asbestos exposure. Without treatment, the average life expectancy is only a few months. Treatment can extend this in certain patients, but mesothelioma is still considered incurable, and long-term remission is very rare.
- Legally Reviewed By: Sam E. Taylor
- Last Modified December 11, 2024
Types of Mesothelioma
There are different types of mesothelioma, which are found in different places in the body.
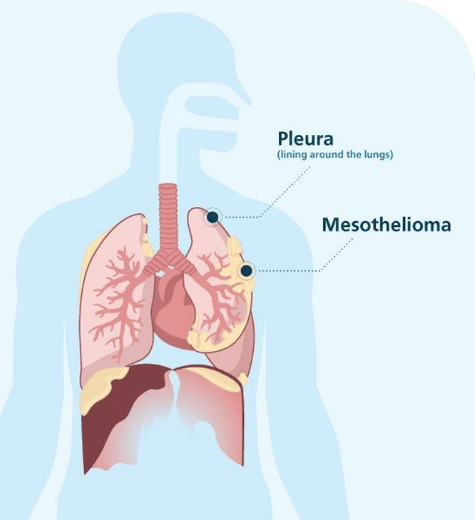
occurs in the pleura, the lining of the lungs. This is by far the most common type, accounting for about 80 percent of all mesothelioma cases.

occurs in the peritoneum, the lining of the digestive system. This is the next most common type, accounting for about 15 percent of mesothelioma cases.
occurs in the pericardium, the lining of the heart. This type is very rare.

occurs in the tunica vaginalis, the lining of the testes. This type is also very rare.
Mesothelioma Risk Factors
The most common cause of mesothelioma is asbestos exposure. More than 80 percent of pleural mesothelioma patients and up to half of peritoneal mesothelioma patients have a known history of asbestos exposure.
Asbestos is a mineral that was used for many years across a wide variety of industries due to its stability and resistance to heat. It tends to break easily into fibers, which can be extremely tiny—so tiny that they can’t be seen, felt, or even smelled when they’re suspended in the air.
Asbestos fibers are naturally long, thin, and sharp. When inhaled, they can become embedded into the lung tissue and work their way into the surrounding pleura. They may also be coughed up and swallowed. Asbestos is so chemically stable that even stomach acid can’t destroy it, and the fibers can embed themselves into the digestive tract and may work their way through into the surrounding peritoneum.

It’s clear that asbestos is strongly associated with the development of mesothelioma, but scientists are still working to understand exactly how the mineral causes cancer. Any foreign substance in the body will naturally provoke an inflammatory response, and asbestos does so in the mesothelium. However, it’s such a stable mineral that the body isn’t able to destroy it.
A stronger and stronger immune response occurs as the body attempts to get rid of the asbestos. This inflammation can eventually lead to scarring, which results in a lung disease known as asbestosis. In addition, it can cause damage to the DNA of cells, which has the potential to lead to cancer. Although asbestos exposure is most strongly linked to mesothelioma, it can also cause other types of cancer, including lung cancer.
It takes many years for asbestos exposure to lead to mesothelioma. This time period, known as the latency period, can be 20 to 40 years or even longer.
Many people were exposed to asbestos at work. Military veterans, industrial workers, construction workers, and firefighters are among those who are most likely to have had workplace asbestos exposure.
The families of workers may also have been exposed because asbestos fibers can travel on a person’s clothing, skin and hair, and then enter the air in the home. This secondary exposure to asbestos is a contributor to mesothelioma in women.
Some people have also had asbestos exposure that wasn’t related to work; for example, some commercial talcum powders have been found to be contaminated with asbestos.
Mesothelioma is relatively rare, accounting for less than 0.3 percent of all cancer diagnoses in the United States. About 3.000 cases are diagnosed every year. This number increased from the 1970s through the 1990s but is now relatively steady, likely because of increased regulation of asbestos.
Although it’s now heavily regulated, asbestos is not completely banned in the United States, and asbestos imports continue to occur.
Mesothelioma Symptoms
The symptoms of mesothelioma are different for each type. These symptoms are often similar to those of other diseases, many of which are more common than mesothelioma. This can lead to a delay in diagnosis.
Pleural Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness of the voice
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats and/or fever
Similar symptoms can be caused by other respiratory diseases, including pneumonia, COPD (emphysema), asthma and lung cancer.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Swelling of the abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats and/or fever
There are a number of other digestive conditions that can cause similar symptoms, including Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, irritable bowel syndrome and colon cancer.
Mesothelioma Diagnosis
The diagnosis of mesothelioma generally involves several different steps, including imaging studies, a biopsy and sometimes blood tests. Collaboration is necessary between oncology, radiology, and surgery in order to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis.
Imaging Studies
For pleural mesothelioma, the diagnostic process often starts with a chest X-ray. This test is useful because it can detect several different types of issues in the lungs, allowing the doctor to narrow in on the diagnosis.
For peritoneal mesothelioma, the first imaging study is often a CT scan of the abdomen. A CT scan also uses X-rays, but the images are more detailed. This allows the doctor to look for various issues in the abdomen. Pleural mesothelioma patients may have a CT scan of the chest, often after concerning findings on a chest X-ray.
Additional imaging studies may also be useful, such as an MRI. Doctors may also order a PET scan, which uses a tracer to detect cancer cells; this is often used to check for metastasis, or spread of the cancer to different parts of the body.

Biopsy
The definitive diagnosis of mesothelioma requires a biopsy. This is a small sample of tissue that’s examined in the laboratory to determine whether there are cancer cells present and, if so, what type.
For pleural mesothelioma, the most common way to obtain the biopsy is through a minor surgical procedure called a thoracoscopy, in which a thoracic surgeon inserts an instrument through small incisions in the chest wall. For peritoneal mesothelioma it’s commonly obtained during a laparoscopy, which involves inserting a scope through small incisions in the abdominal wall.
There are other ways that the biopsy may be performed. Sometimes, the sample can be obtained using a needle inserted through the skin. In other cases, a sample of fluid obtained from a pleural effusion (buildup of fluid around the lungs) or from ascites (buildup of fluid in the abdomen) may contain enough cancer cells for a pathologist to analyze.
Blood Tests (Immunochemistry)
A series of blood tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis. These check for biomarkers, which are certain proteins in the blood. Different proteins are associated with different types of cancer. These blood tests are not accurate enough to diagnose mesothelioma on their own, but they can help to distinguish different types of cancer to ensure that the diagnosis is accurate.
Mesothelioma Cell Types
Another important factor in diagnosing mesothelioma is the cell type of the cancer. There are three main mesothelial cell types:
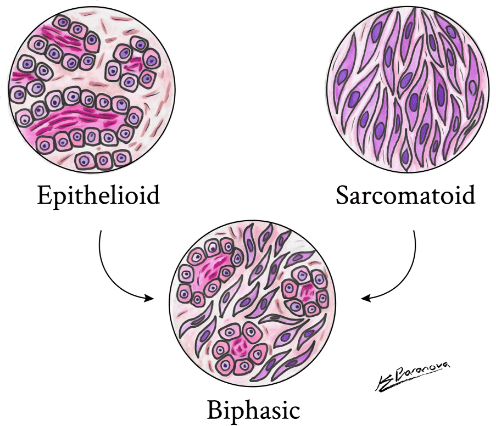
The cells of this type are more regularly shaped and tend to form discrete sheets or clumps. This cell type is generally the easiest to treat and carries the best prognosis.
These cells are more irregularly shaped. They tend to be longer and tapered at both ends, which contributes to their tendency to spread easily. This cell type is the most difficult to treat.
Tumors of this type have characteristics that are intermediate between the other two types.
The cell type of a patient’s cancer has a significant impact on prognosis and treatment options. For example, only patients with epithelioid tumors are candidates for certain types of tumor-removing surgery.
Stages of Mesothelioma
The stage of a cancer refers to how advanced it is. There are various ways to describe a cancer’s stage, which differ depending on the type of mesothelioma.
Pleural Mesothelioma Stages
For pleural mesothelioma, there’s a formally defined staging system called the TNM staging system, which characterizes the cancer by the size of the tumor, spread to lymph nodes and metastasis (spread to distant parts of the body).
Stage 1
is localized to the pleura.
Stage 2
has grown into adjacent organs and/or has spread to local lymph nodes.
Stage 3
has grown into additional tissues and/or has spread to more distant lymph nodes.
Stage 4
has undergone metastasis.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Stages
For peritoneal mesothelioma, there isn’t a formal staging system. One common method uses a modified version of the TNM system. To classify the tumor size, this system uses the peritoneal cancer index (PCI), which is determined by scoring the amount of cancer present in each of 13 different regions of the abdomen, for a maximum score of 39.
Stage 1
has a PCI score of 10 or less.
Stage 2
has a PCI score of 11 to 30.
Stage 3
has a PCI of 31 or higher, and/or spread to lymph nodes or distant organs.
Mesothelioma Prognosis
Mesothelioma is a very aggressive cancer. Without treatment, the average life expectancy is about four to six months.
For those who receive treatment, pleural mesothelioma patients have a median survival of 15 to 22 months, depending on the stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis. For peritoneal mesothelioma patients who receive CRS-HIPEC (a combination of surgery and chemotherapy), median survival rates of 34 to 92 months have been reported.

Mesothelioma Treatment Options
Pleural Mesothelioma Treatment
- Tumor-removing surgery may be used to try to remove as much cancer tissue as possible. Options include extrapleural pneumonectomy and pleurectomy and decortication. This is only an option for patients whose cancers are in early stages.
- Chemotherapy may be given before, during or after a surgical procedure. It may be delivered specifically into the thoracic cavity during surgery or administered to the whole body through an IV.
- Some patients receive radiation therapy, which is often given after surgery to help kill any remaining cancer cells.
- A newer treatment option is immunotherapy. This treatment modality uses the patient’s own immune system to target and destroy the cancer cells. There are two options that are currently FDA-approved for pleural mesothelioma patients. One is a drug called Keytruda, and the other is a combination of Opdivo and Yervoy. At this time, these medications are only approved for specific pleural mesothelioma patients.
- A new device called tumor-treating fields (TTF) was FDA-approved in 2019 to treat patients who aren’t eligible for surgery. This device uses electrical currents passed through the skin to interfere with cancer cells’ ability to grow and divide.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Treatment
For peritoneal mesothelioma, the most effective treatment modality is a combination of surgery and intraoperative chemotherapy known as cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS-HIPEC). Studies have found that this treatment can extend life expectancy from an average of about four months to between 34 and 92 months. Although the procedure carries risks and causes significant side effects, it allows many patients to have a few more years with their family and friends.
Patients who are not eligible for CRS-HIPEC may be treated using systemic chemotherapy, although this is not nearly as effective.
Palliative Treatment for Mesothelioma
Palliative care focuses on quality of life rather than length of life. Some patients are not eligible for life-extending treatment, while others choose to receive only palliative care because they would rather focus on enjoying their remaining time with loved ones rather than endure the side effects of aggressive treatments.
- Thoracentesis to drain excess fluid from around the lungs
- Paracentesis to drain excess fluid from the abdomen
- Pleurodesis, in order to prevent repeated fluid buildup around the lungs, medication, like medical talc, is inserted, which causes the two layers of the pleura to adhere to each other
- Palliative surgery or chemotherapy to shrink tumors that are causing significant symptoms
Clinical Trials
While current treatments are able to extend life for many mesothelioma patients, cancer research continues in an effort to develop new treatments and better combinations of the existing treatments.

- Immunotherapy - While two types of immunotherapy are now FDA-approved for treating certain mesothelioma patients, researchers hope to develop better forms of this treatment.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT) - This uses a drug that’s activated by light in order to kill cancer cells. During surgery, the surgeon shines light of the correct wavelength to activate the medication. PDT is currently being used for certain cancers, and researchers are looking at whether it might be effective for mesothelioma.
- Gene therapy - This form of cancer treatment uses modified viruses to insert particular genes into cancer cells in order to make them easier to kill.
Some mesothelioma patients choose to enroll in a clinical trial, which is a research study of a new treatment (or a new combination of existing treatments). Being part of a mesothelioma clinical trial might give you access to a cutting-edge treatment that’s not yet available otherwise. However, there are also important tradeoffs to consider. We recommend discussing clinical trials with your oncologist.
Cost of Mesothelioma Treatment
The cost of treatment for mesothelioma can be significant. Even for patients who have Medicare or private insurance, the deductibles and copays can quickly add up. Some patients also benefit from using certain complementary treatments, which may not be covered by insurance. With all of these costs, treatment for mesothelioma can become a financial burden for many families.
Many mesothelioma patients have this cancer because they were exposed to asbestos on the job or because a family member unknowingly brought asbestos home from work. Unfortunately, some companies failed to provide their workers with proper protective equipment, even after the dangers of asbestos were known. In many cases, courts have held these companies accountable for the harm that they caused in exposing their workers to a known carcinogen.
Mesothelioma patients who were exposed to asbestos at work may be eligible to receive a financial settlement, which can help ease the financial burden of treatment.
How can The Lanier Law Firm help if I've been diagnosed with mesothelioma cancer?
You may be unaware of how or where you were exposed to asbestos. The Lanier Law Firm specializes in representing mesothelioma victims and those diagnosed with other asbestos-related illnesses.
Our attorneys will obtain a detailed life history to help you identify all sources of exposure. Based on this information, we can help you with the following:
- File a mesothelioma claim in the jurisdiction most advantageous to you
- File trust fund claims on your behalf
- File workers’ compensation claims on your behalf
- Gather the necessary evidence necessary to verify your claim
It is important to contact a mesothelioma attorney as soon as possible after your diagnosis. Every jurisdiction has a deadline, called a statute of limitations, governing when you can file a claim. If this deadline is missed, your legal options may be severely limited. The statute of limitations may be as short as one year in some jurisdictions.
The Lanier Law Firm has experienced mesothelioma lawyers in New York City, Los Angeles, and Houston serving clients nationwide.
By submitting this form, you agree to our terms & conditions. Please read full disclaimer here.